Many EU Member States have adopted high penalties for DAC6 non-compliance, potentially resulting in severe fines in cases of under- and overreporting, especially for intermediaries lacking a structured compliance process. In some countries, intermediaries may even lose their professional licenses when no structured monitoring system is in place.
In many countries, local tax authorities have consistently indicated that the first series of tax audits will initially target internal DAC6 compliance processes ‘as a whole‘. Therefore, having a structured process in place could be required to determine whether a reportable cross-border arrangement (‘CBA‘) can be identified at an early stage and whether arrangement data is processed in a consistent manner.
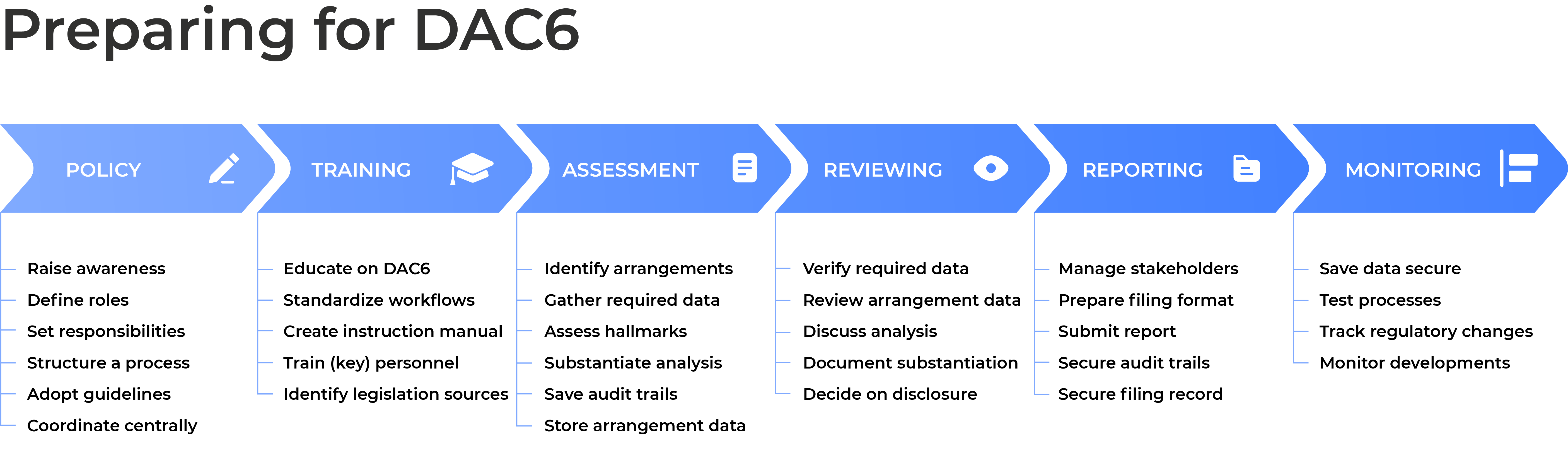
This Top 5 discusses the following five practical considerations to help your organization with the implementation of a structured DAC6 compliance process:
- Develop an internal policy
- Standardize your reporting process
- Manage workflows and stakeholders
- Securely store arrangements and document technical analysis
- Review and update your reporting process
1. Develop an internal policy
(raising awareness and preparing adoption of a firm-wide structured process)
Organizations must raise awareness of DAC6 throughout. First, a general understanding of DAC6 should be obtained. Subsequently, you can learn more about the local mandatory disclosure regulations applicable in your country (domestic legislation). Knowing how local reporting obligations may affect your organization will allow you to determine which internal and external responsibilities must be accounted for.
The company board and management can be informed about DAC6 in general, most notably accounting for the potential penalties and reputational risk. To support, and promote change and compliance throughout your entire organization, key personnel across all service lines must be educated on the domestic legislation and technical application of country-specific elements of DAC6. Additionally, training staff across all service lines can help to familiarize the different reporting steps and assessment of arrangements. In that regard, software solutions can enhance your reporting process, i.e. enhanced efficiency by automating workflows. Furthermore, as some countries allow for electronic filing in XML only, a reporting tool should therefore include an integrated functional feature for XML conversion of DAC6 reports. Regardless of whether software is used, you should:
- raise general awareness by informing personnel
- educate on DAC6 and your country-specific local reporting obligations
- identify technical knowledge resources and consider supporting tools for reporting
- train staff and enshrine best practices using typical case studies
- create a roadmap for implementing a compliance process
- coordinate the compliance process from a central point
2. Standardize your reporting process
(coordinating a consistent approach and have a central point of administration)
It is advisable to adopt an end-to-end reporting process that provides a standardized process to identify, capture, monitor, assess, and store arrangements in a consistent way throughout your entire organization. Each step in the reporting process may comprise multiple workflows, which should always be followed consistently. From gathering data to set clear roles and responsibilities throughout the entire reporting process. You should aim to ensure there will be no missed, late, or inaccurate disclosures, and that potential reportable CBAs can be identified at an early stage and from the beginning endure the same DAC6 compliance ‘funnel‘ resulting in consistent reporting.
Actions to consider when structuring your reporting process:
- standardize how reportable information is collected and processed
- implement a consistent approach within your firm that everyone must follow
- educate key personnel
- implement checks and balances (two-tier reviewing and the four-eyes principle)
- set clear roles and responsibilities in the reporting process
3. Manage workflows and stakeholders
(managing your internal workforce and external stakeholders)
It is important to minimize the administrative burden. Higher key personnel ideally spend the least time on preparatory activities, primarily focusing on the technical application of local country regulations substantiated with detailed DAC6 considerations. Implementation of central overview and controls over the entire reporting process allows you to carry out any necessary adjustments on time during the preparation of arrangements. This also means a secure information system is ideally based on the so-called least-privilege and need-to-know principles. In addition, you can easily manage (external) stakeholders, including clients, tax inspectors (tax audits), or other intermediaries involved.
It is advisable to define job functions and assign tasks in the following processes:
- data collection of the required information
- implementation of a two-tier, four-eyes principle-based hallmark assessment
- documentation of technical elements (substantiation analysis)
- determine outcome DAC6 analysis and decide on disclosure
- actual disclosure of reportable CBA to local tax authorities
- manage (external) stakeholders (intermediaries or tax inspectors)
4. Store arrangements and document technical analysis
(securely storing arrangements per client, including hallmark assessments and audit trails)
For maximum DAC6 compliance, your reporting process should be audit-ready and provide full transparency in how your organization records arrangements and performs its DAC6 analyses, including a full history log of all changes (audit trails) easily accessible to stakeholders.
- prepare country-specific templates to gather data and prepare arrangements
- save arrangements in a central data environment, per client/business vertical/group company
- centralize your (digital) data repository and secure information systems in use
- discuss any grey area-cases and substantiate decisions based on a defendable standpoint
5. Review and update your reporting process
(tracking regulatory changes and aligning your DAC6 process with the latest MDR obligations)
The use of typical case studies during staff trainings will help educate your personnel and enshrine best practices within your organization more easily. In addition, it is advisable to create instruction manuals or guidelines to support key personnel and guarantee a consistent approach. Identify relevant resources and provide easy access for personnel, as it is crucial to track regulatory changes on time and monitor developments. Subsequently, you will continuously perform adjustments required to adopt the latest DAC6 changes or local interpretations because your organization’s processes and policies must reflect the latest state of play, ensuring DAC6 compliance.
Maintain healthy levels of DAC6 compliance with your reporting process by:
- testing all processes to identify, capture, monitor, assess, and store arrangements adequately
- maintaining internal guidelines or instruction manuals for (key) personnel reflecting the latest rules
- tracking regulatory changes from each jurisdiction and other developments
- updating your staff and clients about notable developments